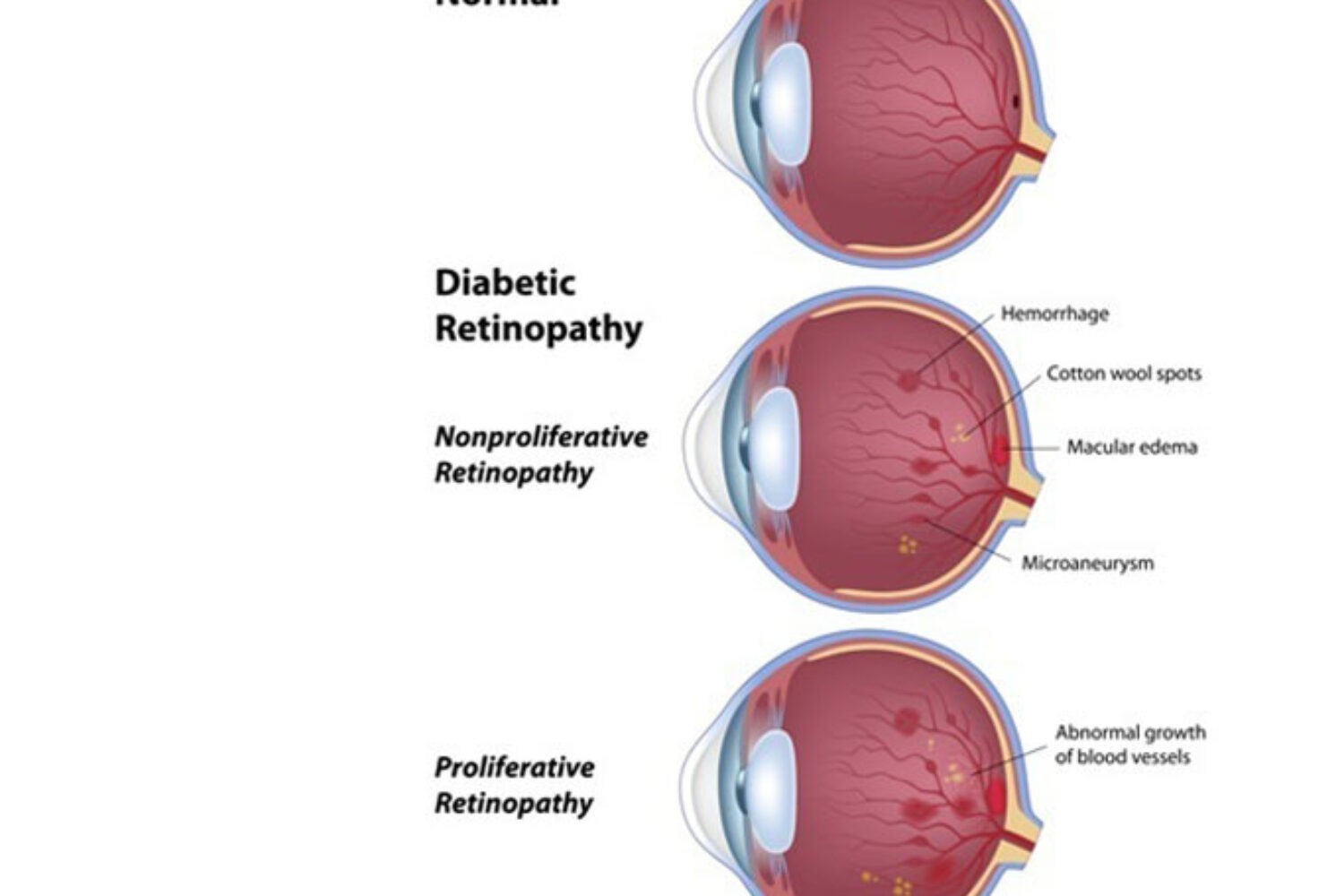
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that is caused by changes in the blood vessels of the eye. The retina is a nerve layer at the back of the eye that senses light and helps to send images to your brain. When blood vessels in the retina are damaged, they may leak fluid or blood, and grow fragile, brush-like branches and scar tissue. This can blur or distort the images that the retina sends to the brain.
Diabetic Retinopathy is the leading cause of new blindness among adults in the United Stated. People with untreated diabetes are said to be 25 times more at risk for blindness than the general population. The longer a person has diabetes, the more the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy increases. People with Type 1, or juvenile diabetes are more likely to develop diabetic retinopathy at a younger age.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy treated?
As there are no symptoms to diagnose, the best protection is to have regular eye examinations. You doctor will consider your age, your medical history, your lifestyle, and how much your retina is damaged to determine treatment. In many cases, treatment is not necessary, but you will need to continue regular eye examinations. In other cases and more advanced stages of the disease (proliferative retinopathy), laser surgery is often helpful.